Test phases 5 and 6: Data on seroprevalence and extent of immunity
The 5th and 6th test phases of Corona Immunitas took place in the cantons of Zurich, Ticino and Vaud (phase 6 only) in March 2022 and June/July 2022. In addition to the antibody test, we performed neutralisation tests against the Wild Type as well as variants relevant for Switzerland (including Omicron). Neutralising antibodies bind to sites of the SARS-CoV-2 virus where the virus can enter human cells. In the digital follow-up, we collected data on SARS-CoV-2 infections, symptoms, vaccination and Long Covid symptoms every two months.
At the beginning of March 2022, seroprevalence was 98% in the general population, with no relevant differences across cantons and age groups. Most study participants (92.1%) showed high antibody levels and had neutralising antibodies, 95% against Wild Type SARS-CoV-2, 91% against the Delta variant and 87% against the Omicron variant. These values indicated high immunity in the population at about two months after the start of the Omicron wave in Switzerland. The results of phase 5 were published in the Eurosurveillance journal.
At the beginning of July 2022, i.e. after the first large Omicron wave ended in Switzerland, we found unchanged high levels of seroprevalence and immunity. 98% of study participants showed antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, 94% showed high antibody levels, and most individuals showed neutralising antibodies to the variants (93% to Wild Type, 91% to Delta and 84% to Omicron).
Of particular interest was the extent of hybrid immunity, i.e. immunity induced by a combination of infection(s) and vaccination. We estimated hybrid immunity to be at least 50% in early July 2022. There was a clear increase in hybrid immunity between March and July 2022. Figure 1 shows these results in the epidemiological context of Switzerland.
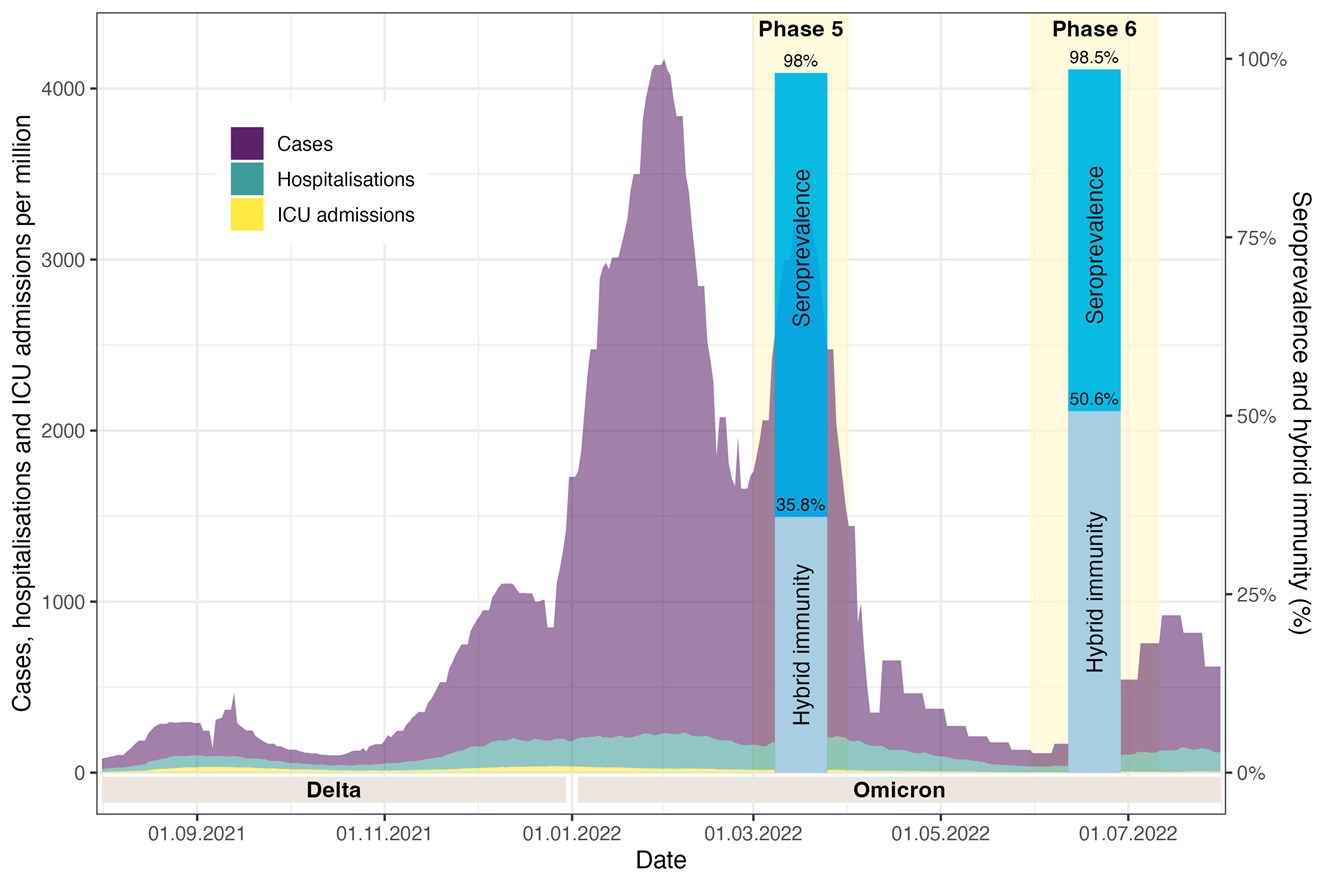 Fig. 1: Epidemiological context in Switzerland from September 2021 to July 2022 and seroprevalence and hybrid immunity in the population of the cantons of Zurich, Vaud and Ticino (based on Frei et al, International Journal of Epidemiology, 2023; https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyad098).
Fig. 1: Epidemiological context in Switzerland from September 2021 to July 2022 and seroprevalence and hybrid immunity in the population of the cantons of Zurich, Vaud and Ticino (based on Frei et al, International Journal of Epidemiology, 2023; https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyad098).
These results on functional and hybrid immunity in the Swiss population after the Omicron waves showed that SARS-CoV-2 has become endemic. The results of phase 6 are published here.
Additional findings:
Cellular immune responses in individuals with different vaccination and infection status
In addition to humoral responses (antibodies) following SARS-CoV-2 infection, we also examined the cellular response, i.e., T-cell responses to the spike, membrane, and nucleocapsid proteins, in individuals with different vaccination and infection statuses using an assay called the interferon-gamma release assay. In March 2022, spike IgG responses could be detected in almost all participants, as was the case for spike IgG antibodies, with no significant change until July 2022. In contrast, T-cell responses against the membrane and nucleocapsid proteins increased significantly until July 2022, indicating viral (re)exposure. Thus, this assay may complement antibody tests, particularly for the nucleocapsid protein, as recent infections may be detected more reliably with this interferon-gamma release assay. Thus, hybrid immunity may also be estimated more accurately. The article can be found here.
Association of coronavirus infections and cognitive functions in elderly individuals
Elderly participants (≥65 years of age) from the general population of the Canton of Zurich and participating in Corona Immunitas were enrolled in a substudy in which additional standardized cognitive tests were performed. Results showed that individuals with SARS-CoV-2 antibodies related to vaccination had better cognitive function than individuals with antibodies due to infection, particularly in the areas of language comprehension and temporal orientation. For those interested, click here for the full article.
Influence of economic resources on mental health
In another study, we examined the influence of changes in financial resources and employment situation on the mental health of 1759 participants during and after the second COVID-19 wave. Results showed that persistently low financial resources were associated with poorer mental health. Among study participants who perceived the national economic situation as worrisome, the negative effects on mental health were more pronounced. This underscores the link between economic stress and mental health during the pandemic. All additional information on the study can be found here.
Seroprevalence and risk factors over time
This study investigated the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and risk factors for seropositivity in different Swiss regions between May 2020 and September 2021. In the first phase of the pandemic, younger age was the only risk factor for seropositivity. In later phases and after the start of the vaccination campaign, older age, high income, obesity, concomitant diseases, and retirement were associated with higher seropositivity. However, when vaccination status was taken into account, these associations were no longer found and there were no differences between groups. Click here for the full article.
Seropositivity in adults living with children
In addition, we investigated in eleven cantons whether seropositivity among adult Corona Immunitas participants depended on whether or not they lived with children in the same household. The results suggest an association, especially for younger and multiple children in the same household and for men. For more information, go to the full article here.